Theory of Art
Theory for a better understanding of art
Way to Wealth
Man does not live from art alone
An inspirational speech by the fictional father Abraham on the use of capital. Humorously rendered by the author Benjamin Franklin.
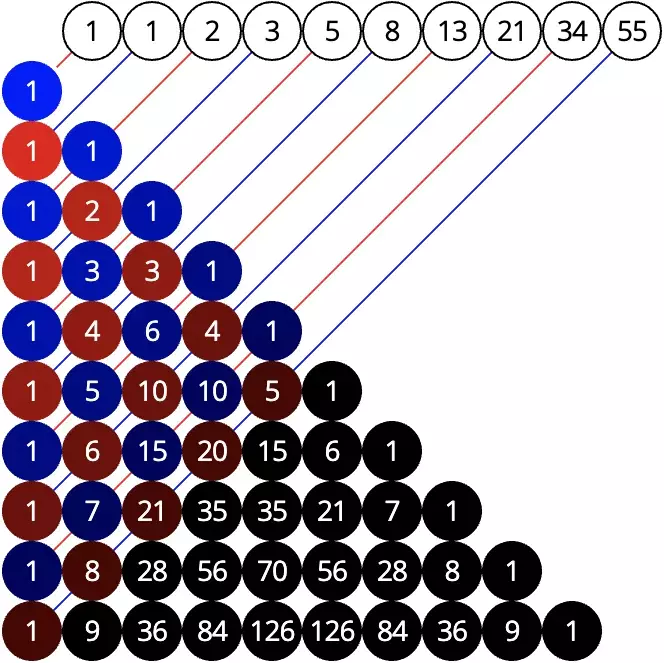
Pascal's triangle, Fibonacci sequence and golden section
More than just a template for solving binomial formulas
A less frequently mentioned property of Pascal's triangle - the representation of the Fibanocci numbers as the sum of the numbers lying on a diagonal of 45° in the left-centered triangle - is listed here.
About Pascal's triangle and golden section
Experiment on the calculation of probability
The law of large numbers
Applied practically, this experiment makes clear the decreasing influence of chance with many repetitions of a process.
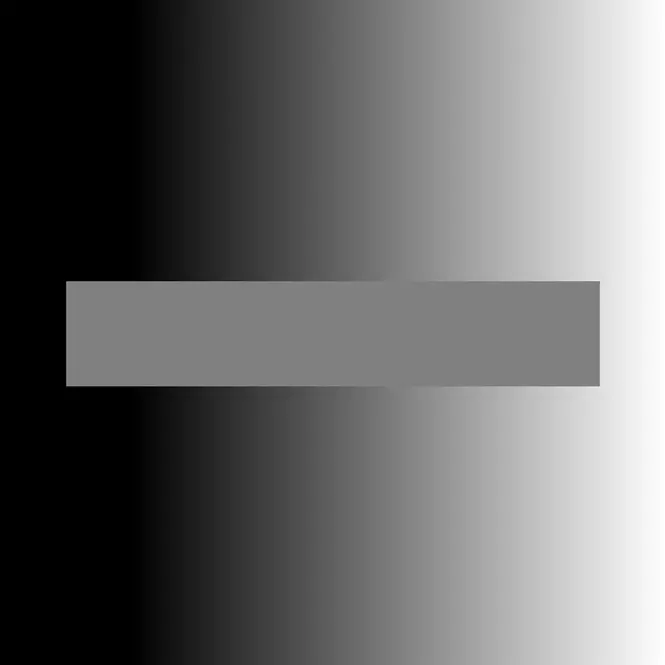

Optical illusions
Not everything is as it seems
Practical examples of optical illusions for use in the visual arts.
See Optical illusions